Comprehensive Analysis of DeepSeek V3 - Open Source AI
Discover DeepSeek V3, an open-source AI offering high efficiency and power. Learn how it can be applied to your AI projects.
Released in December 2024, it stands out as a powerful open-source model designed to compete with leading closed-source models like OpenAI's GPT-4o and Anthropic's Claude-3.5-Sonnet. You can chat with DeepSeek V3 and 30+ other AI models on Okara.
Its Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture, with 671 billion total parameters and 37 billion activated per token, ensures high performance while keeping computational costs low, making it accessible for a wide range of users.
Model Architecture and Training
DeepSeek V3 builds on the Transformer framework, incorporating Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA) for efficient computation and DeepSeekMoE for cost-effective training. It introduces auxiliary-loss-free load balancing and multi-token prediction, enhancing its ability to generate coherent text. Trained on 14.8 trillion high-quality tokens, it underwent Supervised Fine-Tuning and Reinforcement Learning, costing about $5.6 million and requiring 2.788 million GPU hours, a fraction of what competitors like GPT-4 reportedly cost.
Performance and Applications
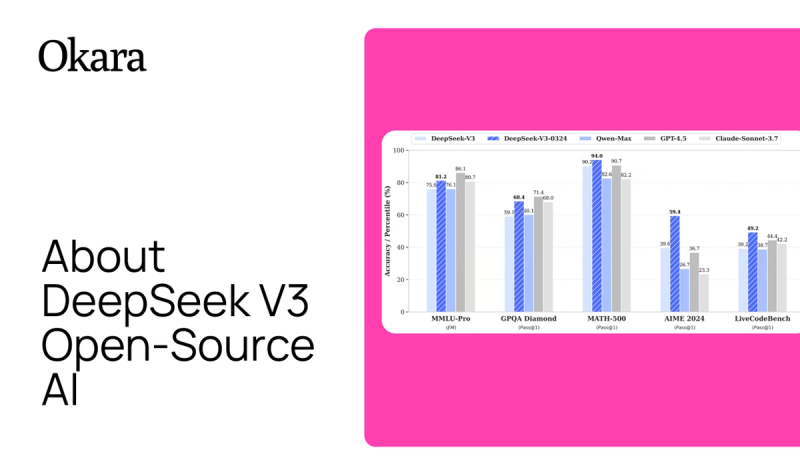
Evaluations show DeepSeek V3 excels in math (61.6% on MATH), coding (65.2% on HumanEval), and language tasks (88.5% on MMLU), often surpassing other open-source models like LLaMA-3.1 and Qwen2.5. It’s suitable for chatbots, content creation, code assistance, and educational tools, with its efficiency enabling deployment in resource-limited settings.
Comparison and Future Outlook
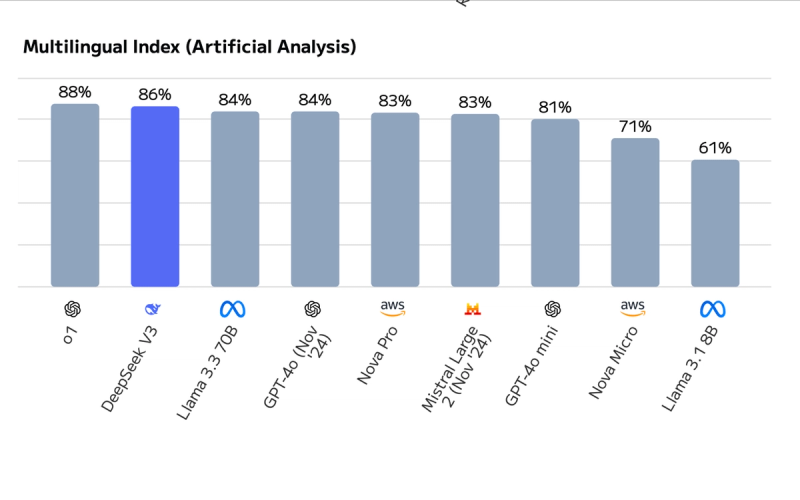
Compared to closed-source models, DeepSeek V3 offers similar performance at a lower cost, thanks to its open-source nature and MoE design. DeepSeek plans to add multimodal support, potentially expanding to image and audio processing, aligning with their AGI goals.
Comprehensive Analysis of DeepSeek V3
DeepSeek V3, launched by DeepSeek in December 2024, is a significant advancement in open-source AI, aiming to bridge the gap with closed-source models like GPT-4o and Claude-3.5-Sonnet. The model's development reflects DeepSeek's mission to democratize AI, with a focus on long-termism and inclusive AGI, as highlighted on their official website (DeepSeek). Given the current date, March 25, 2025, it’s clear both DeepSeek V3 and its subsequent variant, DeepSeek-R1 (released January 2025), are already in use, but this analysis focuses on V3 as per the query.
Technical Details of The Model Architecture
DeepSeek V3 is a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) language model with 671 billion total parameters, but only 37 billion are activated per token, a design choice for efficiency. It builds on the Transformer framework, incorporating:
- Multi-head Latent Attention (MLA): With an embedding dimension of 7168, 128 attention heads (each 128-dimensional), KV compression to 512, query compression to 1536, and a decoupled key/query dimension of 64, MLA optimizes computational efficiency, as detailed in the GitHub repository (DeepSeek-V3 GitHub).
- DeepSeekMoE: Comprising 61 layers, the first three use dense feed-forward networks (FFNs), while others employ MoE with one shared expert, 256 routed experts, and eight activated per token. The intermediate dimension is 2048, with node-limited routing to four nodes, enhancing scalability.
- Auxiliary-loss-free Load Balancing: This strategy, pioneered in DeepSeek V3, minimizes performance impact by balancing expert utilization without auxiliary losses, a technique validated in prior models like DeepSeek-V2.
- Multi-token Prediction (MTP): Trained to predict one additional token with a shared embedding/output head, maintaining causal chains, this enhances generative capabilities, with a depth of 1 and high acceptance rates (85-90% for the second token).
These innovations, also discussed on Hugging Face (deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V3), make DeepSeek V3 computationally efficient, suitable for resource-constrained environments.
Training Process: Rigorous and Cost-Effective
The training process was extensive, pre-training on 14.8 trillion diverse, high-quality tokens, followed by Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). Key details include:
- Optimizer and Hyperparameters: Used AdamW with β1=0.9, β2=0.95, weight decay=0.1, and a maximum sequence length of 4K.
- Learning Rate Schedule: Started at 2.2×10^-4, constant to 10 trillion tokens, then cosine decayed to 2.2×10^-5 over 4.3 trillion, final adjustments to 7.3×10^-6.
- Batch Size: Increased from 3072 to 15,360 in the first 469 billion tokens, then maintained at 15,360.
- Auxiliary-loss-free Parameters: Bias update speed γ=0.001 for first 14.3 trillion tokens, 0.0 for last 500 billion, balance loss α=0.0001.
- MTP Loss Weight: λ=0.3 for first 10 trillion, 0.1 for last 4.8 trillion.
- Long Context Extension: Used YaRN in two phases, first to 32K then 128K, with specific learning rates and batch sizes, as outlined in the API docs (DeepSeek API Docs).
The total training cost was 2.788 million H800 GPU hours, costing approximately $5.576 million at $2/GPU hour, significantly lower than competitors like GPT-4 ($100 million) and Meta's LLaMA 3.1, as noted on Wikipedia (DeepSeek Wikipedia).
Performance and Evaluation: Benchmark Results
DeepSeek V3’s performance was rigorously evaluated, with results surpassing other open-source models and nearing closed-source leaders. Key metrics include:
BenchmarkScoreContextMMLU (5-shot EM)87.1% (pre), 88.5% (post)Language understandingMATH (4-shot EM)61.6%Mathematical reasoningHumanEval (0-shot P@1)65.2%Code generationGSM8K (8-shot EM)89.3%Grade school mathArena-Hard Win Rate85.5%Open-ended tasksAlpacaEval 2.0 Win Rate (length-controlled)70.0%Chat evaluationRewardBench Average87.0Chat, safety, reasoning scores
Post-training, it achieved 89.1% on MMLU-Redux and 75.9% on MMLU-Pro, with specific improvements in reasoning tasks like LiveCodeBench-CoT (Pass@1 from 31.1 to 37.4) and MATH-500 (Pass@1 from 74.6 to 83.2), as per the technical report. It outperforms DeepSeek-V2-Base, Qwen2.5 72B, and LLaMA-3.1 405B, especially in math and code.
Applications and Use Cases
DeepSeek V3’s versatility enables applications across sectors:
- Conversational AI: Powers chatbots and virtual assistants, with high scores in Chat (96.9 on RewardBench).
- Content Creation: Generates coherent articles and stories, leveraging its language generation capabilities.
- Code Assistance: Supports developers with coding tasks, scoring 65.2% on HumanEval, ideal for programming support.
- Educational Tools: Assists in explanations and problem-solving, with strong performance on educational benchmarks like MMLU.
- Customer Support: Automates responses, enhancing efficiency with its safety score of 87.0 on RewardBench.
Comparison with Other Models
DeepSeek V3’s open-source nature, trained at $5.576 million versus GPT-4’s $100 million, offers a cost-effective alternative. It matches closed-source performance, with an 85.5% win rate on Arena-Hard, the first open-source model above 85%, bridging the gap, as per the technical report. Its computational efficiency, activating only 37B parameters per token, contrasts with denser models, making it faster and more energy-efficient, a point emphasized on Wikipedia.
Future Directions and Community Impact
DeepSeek plans multimodal support, potentially integrating image and audio, as hinted in API docs. Their open-source approach fosters community collaboration, with models like DeepSeek-R1 (based on V3, focused on reasoning) showing ongoing innovation. This aligns with their AGI goals, aiming to narrow the open-closed model gap, as noted in various sources.
Conclusion
DeepSeek V3 is a landmark in open-source AI, combining advanced architecture, cost-effective training, and competitive performance. Its applications span multiple domains, with future expansions promising broader capabilities. This model exemplifies DeepSeek’s commitment to accessible, high-performance AI, poised to influence the AI landscape significantly.
Get AI privacy without
compromise
Chat with Deepseek, Llama, Qwen, GLM, Mistral, and 30+ open-source models
Encrypted storage with client-side keys — conversations protected at rest
Shared context and memory across conversations
2 image generators (Stable Diffusion 3.5 Large & Qwen Image) included